General Guidelines and feeding tips for baby’s first year!
BIRTH TO 6 MONTHS

What baby does?
- Sucks and swallows breastmilk and formula
- Pushes tongue out of the mouth when they swallow
New Foods:
- Feed only breastmilk or formula with iron
What to do?
- Be patient
- Feed when your baby is hungry
- Learn your baby’s hunger and fullness cues
AROUND 6 MONTHS

What baby does?
- Sits with help
- Supports and controls head
- Can grasp an object and put it in mouth
- Opens mouth for a spoon
- Can keep most of the food in their mouth
- Removes food from a spoon with a sucking action
- Turns head away when full
New foods:
- Try jarred or home-prepared single-ingredient foods like:
- Pureed fruits, vegetables, or meats
- Infant cereal
What to do?
- Continue breastfeeding or giving formula with iron
- Feed with a spoon
- Start with a smooth and thin texture
- Never put cereal in the baby’s bottle
- Follow baby’s lead. Let your baby show you when they are full.
- Wait two to three days between feeding new foods.
7 – 9 MONTHS

What baby does?
- Sits without help
- Moves food from front to back of the mouth
- Begins side to side movement of the tongue
- Begins to grasp objects with the whole hand and transfer from one hand to another
- Starts to mash food with gums
- Brings head towards the spoon
- Drinks from cup with lots of spilling
New foods:
- Plain, cooked, home-prepared foods, strained or mashed with a fork.
- Try fruits, vegetables, and meats.
- Yogurt, cottage cheese
- Very small pieces of hard cheese.
What to do?
- Continue to breastfeed or give formula with iron.
- As baby gets better at eating, mix food to a thicker texture
- Offer breastmilk or formula in small amounts from a cup
10 – 12 MONTHS

What baby does?
- Picks up food with thumb and forefinger
- Rotary or grinding chewing begins
- Drinks from cup with less spilling
New foods:
- Small pieces of bread, cheese, noodles, crackers, soft tortilla
- Small pieces of cooked, tender, lean meat
- Soft cooked pieces of beans and vegetables
- Pieces of raw, soft, ripe fruits
What to do?
- Continue to breastfeed or give formula with iron
- Offer finger foods
- Watch baby closely while eating
- Keep baby seated in a chair, high chair, or carrier
KEEP IN MIND
- Be patient. It may take more than one time for your baby to like a new taste or texture.
- Begin with small amounts of foods. Offer seconds if needed.
- Do not force your baby to eat or finish all of their food. Turning their head, closing their mouth, shaking their head, or leaning back are signs your baby is full.
- Continue to breastfeed or give formula after solid foods are introduced.
Be sure your baby is drinking enough breastmilk or formula.
- If your baby is ready for table food, spoon out the amount they will eat before adding salt, sugar, fats, or other seasonings to the food for your family.
- Set a good example. Older babies will want to eat what you eat.
- If you have a family history of allergies, there may be foods you want to avoid giving your baby. Check with your doctor or clinic. Signs of an allergic reaction include skin rash, vomiting, diarrhea, irritability, or wheezing.
BE AWARE
- NEVER give honey to your baby. Honey may have botulism, a germ that can be deadly for your baby.
- Do NOT put your baby to bed with a bottle.
- These foods may be choking hazards in babies and children younger than 4 years old:
- Whole hotdogs
- Whole grapes
- Popcorn
- Chunks of peanut butter
- Peanuts and other nuts
- Raw hard vegetables
- Round, hard or sticky candies
Signs your Baby May Be Hungry:
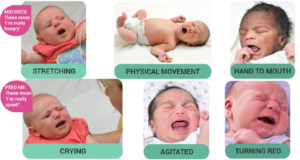
- Getting hungry:
- Stretching
- Physical Movement
- Hand to Mouth
- Feed Me:
- Crying
- Agitated
- Turning Red
Choking Hazards for Children Under One Year:

- Thickly spread nut butters
- Whole nuts and seeds
- Popcorn
- Raw carrots and other hard raw veggies
- Whole grapes
- Tortilla and other hard chips















